Why Do Speakers Have Magnets?
Have you ever wondered why speakers have magnets? These essential components might seem mysterious, but they’re crucial to how we experience sound. If you’re curious to find out what role magnets play in your favorite audio equipment, you’re at the right place! Let’s dive in and learn about the fascinating mechanics behind our daily dose of melodies.
In the sphere of sound technology, magnets function as the powerhouse that transforms electrical energy into sound energy.
Throughout this article, we’re going to cover the following key topics:
- The purpose of magnets in speakers
- How do magnets contribute to speaker functionality?
- The types of magnets used in speakers;
- A detailed look into the interaction between magnets and the voice coil in speakers
- The advantages of using magnets in speaker design.
But before we dive deep, let’s understand why magnets are essential in speaker design. As the forces of attraction and repellence come into play, they create vibrations—pulsating movements of the speaker’s cone that radiate sound waves into the surrounding air.
These vibrations, which our ears interpret as music, speech, and other sounds, result from the complex interplay between electricity, magnetism, and the speaker’s components. It’s a beautifully intricate process, and we’re thrilled to share it with you. Welcome to our magical journey through the world of sound!
Read also: How To Take Apart Bluetooth Speakers With No Screws?
What is the purpose of magnets in speakers?
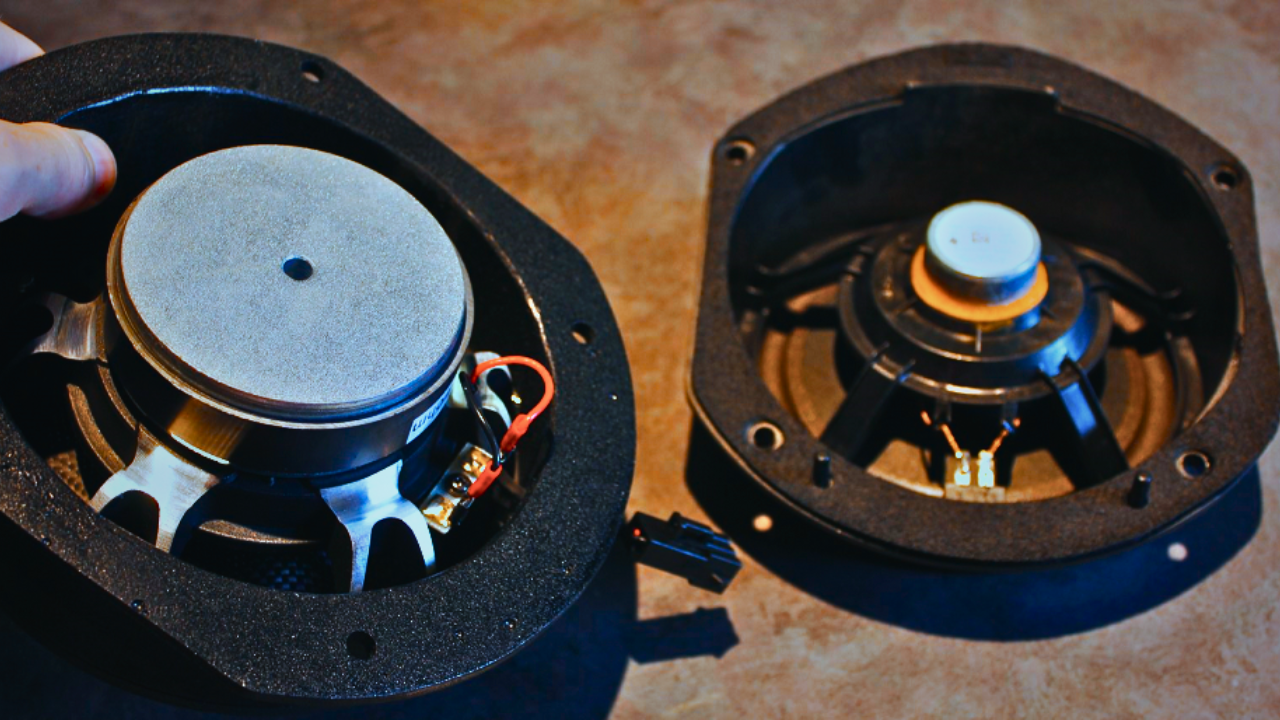
Every time you groove to your favorite music booming from your speakers, have you ever pondered the unsung hero that makes it all possible—the magnet? Just like the heart in our body, the magnet is central to a speaker’s functionality and performance. Let’s dive deep inside your speakers to comprehend what magnets actually do.
Well, for starters, magnets in speakers generate the magnetic field that is essential in creating sound waves. It’s an unsaid fact, but sound is a form of energy, and for this energy to be channelled into beautiful music or engrossing dialogs in a movie, we need to convert an electrical signal into sound waves. And that’s precisely where magnets step in.
Magnets, paired with a voice coil, work in tandem to transform the electrical energy from your power source into mechanical energy. This process is how the vibrations that produce the sounds we hear are created. When electricity passes through the voice coil in the presence of this magnetic field, it generates a force that leads to the movement of the coil and the attached speaker cone.
This movement pushes and pulls the air in front of the speaker, creating the pressure waves that your ears perceive as sound. In a nutshell, without a magnet, your speaker wouldn’t be anything more than an ornament.
It’s mind-boggling, isn’t it? Only then do we realize the profound role of an usually overlooked component when we tear down the walls and peep inside our everyday gadgets. So the next time your speakers bring life to a party or enhance your music experience, remember the integral part played by the magnet hidden inside.
How do magnets contribute to the functionality of speakers?
Magnets truly are at the heart of your speaker’s operation. They play an instrumental role in transforming electrical energy into sound energy. Here’s a simple rundown of the process:
- An audio signal passes from the amplifier through the speaker wire to the speaker.
- This signal, being an electrical one, creates an electromagnetic field around the voice coil.
- The polarity of the magnetic field around the voice coil shifts in response to the positive and negative charges of the electrical audio signal.
- As the voice coil’s magnetic field’s polarity shifts, it is either attracted to or repelled by the permanent magnet’s field.
- This causes the voice coil and attached speaker diaphragm to move back and forth—vibrate—creating pressure waves that we interpret as sound.
In essence, magnets contribute to speakers’ functionality by creating a magnetic field that interacts with the voice coil’s electromagnetic field. This interaction amplifies the audio signal, causing the speaker cone to vibrate and produce sound.
In other words, without magnets, there would be no way for speakers to transform an electrical audio signal into sound waves. The result? Pure silence.
Imagine sitting in your car or in front of your stereo at home, turning up the volume, and hearing nothing. It’s quite disconcerting, isn’t it? That’s the importance of magnets in speaker functionality!
What types of magnets are commonly used in speakers?
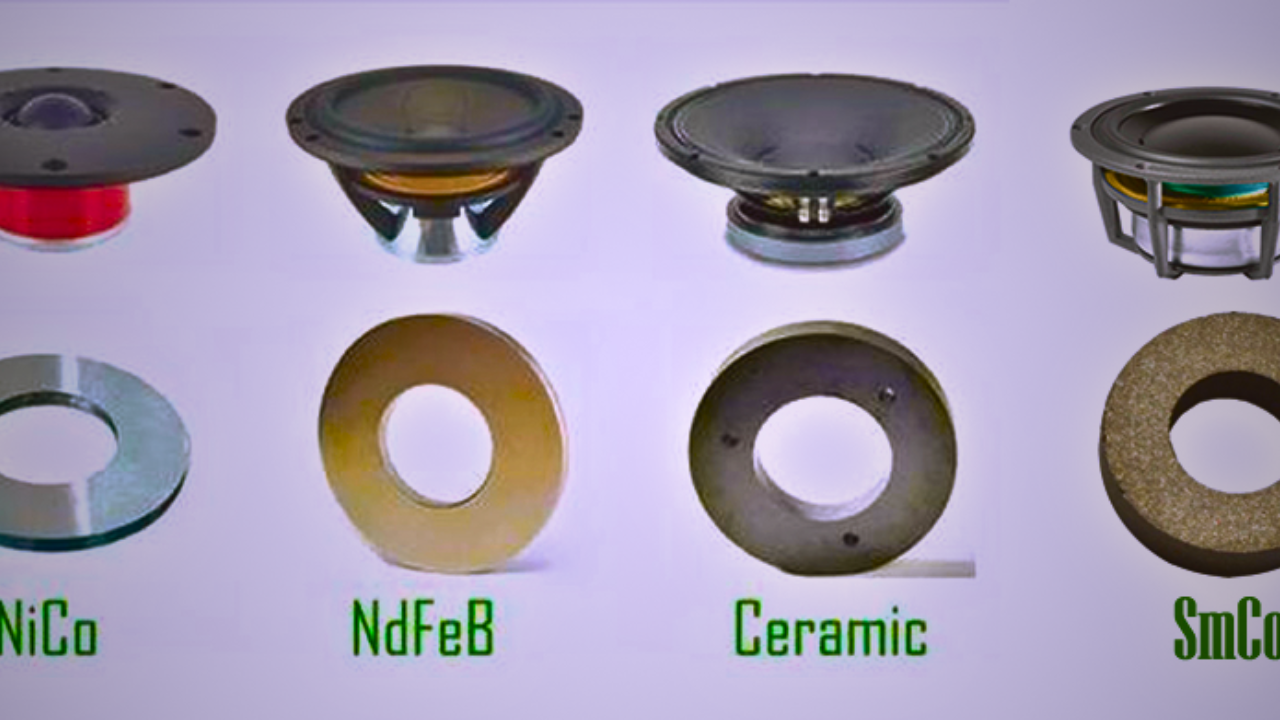

When it comes to the heart of speakers, the type of magnets used matters as much as their purpose and function. The commonly used types of magnets in speakers are alnico, ceramic, and neodymium magnets. Let’s dive a bit deeper into these.
Alnico Magnets:

Alnico magnets are made from an alloy of aluminum, nickel, and cobalt, hence the name. They were the most popular choice for loudspeakers before the invention of cheaper alternatives. They possess great temperature stability and a high magnetic flux density, which enhance sound quality. However, these come with a higher price tag.
Ceramic or Ferrite Magnets:

Ceramic or ferrite magnets are made from strontium or barium ferrite. These have become the go-to choice for most manufacturers due to their inexpensive nature and adequate magnetic field for general-purpose speakers. Although bulkier and weaker than both Alnico and Neodymium magnets, their low cost makes them a popular choice for home audio systems.
Neodymium Magnets:

Neodymium magnets are considered the strongest type of permanent magnet commercially available. They are more powerful and lighter than both alnico and ceramic magnets, but they are also more expensive. Today, they are mainly used in small, high-performance speakers such as headphone speakers and portable Bluetooth speakers.
Even though each of these types has its pros and cons, the choice of magnet often depends on the specific needs of the speaker design. From amplifier speakers using Alnico magnets to home audio speakers choosing ceramic ones and portable speakers going for Neodymium, it’s clear that different magnets serve different purposes.
Read also: How To Connect Speakers To A Monitor?
How do magnets interact with the voice coil in speakers?
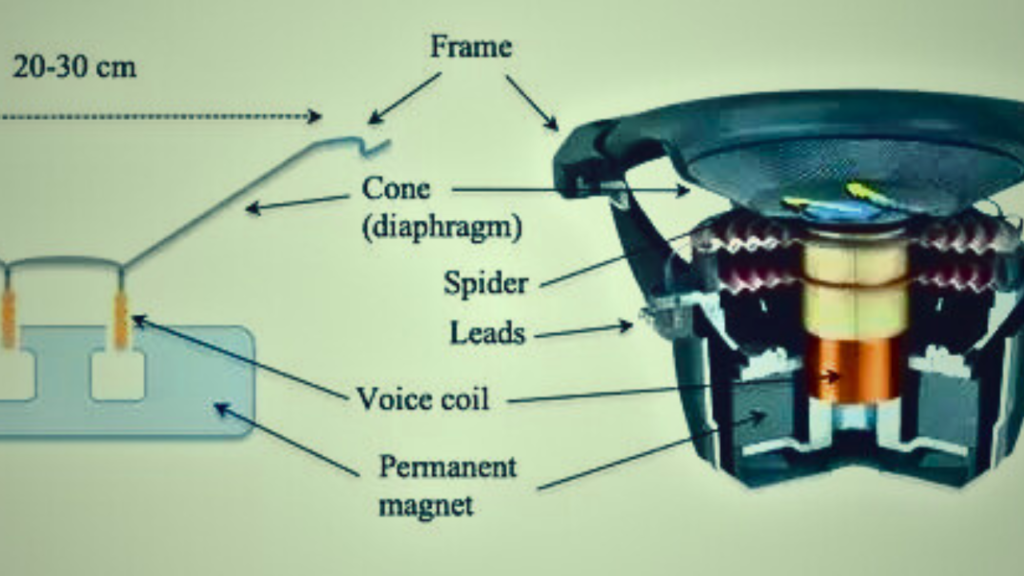
Speaking of a speaker’s internal workings, you’re likely to run into a key component: the voice coil. You might wonder how this voice coil ties into the grand scheme of things. The heart of the matter rests in the fascinating interplay between the voice coil and the magnet.
When an electrical signal, representing an acoustic signal, is sent to the speaker’s voice coil, it generates a magnetic field around the coil. This interaction is governed by the rules of electromagnetism. Think of the voice coil as a temporary magnet whose strength and polarity depend on the direction and magnitude of the electrical signal from the audio source.
Now, this is where the fun part begins. Remember that permanent magnet we discussed earlier, sitting silently at the bottom of your speaker? The voice coil’s generated magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of this permanent magnet. If the voice coil’s magnetic field is identical to that of the permanent magnet, the coil is repelled. However, if it’s the opposite, the coil gets attracted. This back-and-forth movement of the voice coil, thanks to the variations in the audio signal, is what moves the speaker diaphragm, producing the pressure waves that your ears interpret as sound.
In a nutshell:
- audio signal creates a temporary magnetic field in the voice coil
- The induced magnetic field either attracts or repels against the permanent magnet’s field
- The interplay results in the movement of the voice coil
- This movement vibrates the speaker diaphragm, creating audible sound waves
That’s the crux of how a magnet and a voice coil bring your music, podcasts, or movies to life! The application of magnetism to producing sound isn’t just an example of scientific ingenuity; it’s at the heart of how we interact with the world of audio every day.
What are the advantages of using magnets in speaker design?
You’re probably wondering now: Why exactly do speakers have magnets? Good question! The whole point of using magnets in speaker design essentially boils down to their role in generating sound. There are many benefits that come with this integration, centered on efficiency, consistency, and overall audio output quality.
Let’s delve a little deeper and appreciate the various advantages of employing magnets in speaker technology:
- High Efficiency: Functioning as the primary force generator, magnets facilitate the conversion of electrical power to mechanical power—or, simply put, they convert electrical signals into sound. This process is significantly efficient and consumes less power compared to alternatives, thereby enabling the speaker to function optimally for extended durations.
- Consistent Performance: Consistency is key when it comes to sound production, and who does it better than magnets? Their pulling and pushing actions, driven by the current through the voice coil, are stable and predictable, providing a consistent sound output over time.
- Flexibility in Design: Despite their crucial role, magnets do not predetermine the speaker’s size. They allow for different speaker sizes and designs, enhancing innovation and customization possibilities to meet the varying preferences of users.
- Quality Sound: Thanks to the presence of magnets, speakers can reproduce a wide range of frequencies with high fidelity. This results in an audio output that is the closest possible reproduction of the original recording, giving your ears the pleasure of getting lost in the details.
Keep in mind that, despite the role of magnets being quite pivotal, the overall quality and performance of a speaker also depend on various other factors, such as the speaker design, size, shape, and materials used in construction. But one thing’s for sure: without the interplay of magnets in your speakers, getting your daily dose of tunes wouldn’t be quite the same!
Conclusion
In conclusion, to wrap things up, it’s clear to see that magnets play an instrumental role in the operation of speakers. Without them, the sound you relish every day, whether it’s your favorite song, the soundtrack of a movie, or the audio of an engaging podcast, would not be feasible.
Magnets, working harmoniously with the voice coil and other components, create the mechanical movement necessary to produce sound. Through the constant push-pull activity given by the magnet’s field interacting with the electric current in the voice coil, sound waves are generated and amplified to an audible level, allowing you to experience the rich spectrum of tones and pitches in the audio world.
There are numerous types of magnets typically employed in speaker design, but the most common ones are ferrite and neodymium. These magnet types have specific characteristics that make them ideal for use in speakers, with neodymium noted for its exceptional power and compactness and ferrite for its cost-effectiveness.
The advantages of using magnets in speakers are manifold. Primarily, they provide the force needed to move the speaker cone back and forth rapidly, resulting in sound. Additionally, the use of magnets allows for the creation of compact and efficient devices, which enables the proliferation of audio technology in myriad forms, from headphones to home theaters, from smartphones to massive public address (PA) systems.
Given their crucial role and array of benefits, the magnets are an ingenious piece of engineering behind the speakers. Their significance is a testament to the remarkable marriage between science and technology, which brings us dazzling experiences through the power of sound.
Read also: What Is The Difference Between 2-way And 3-way Speakers?
FAQs
Can a speaker work without magnets?
No, a speaker cannot work without magnets. Magnets form an essential part of the speaker by creating a magnetic field in which the voice coils move, resulting in sound production.
What happens if the magnets in a speaker are weak?
If the magnets in a speaker are weak, it can drastically affect the speaker’s performance. Weak magnets likely lead to reduced volume and sound quality due to the dwindling force exerted on the voice coil.
Can you replace the magnets in speakers?
Yes, you can replace the magnets in speakers. However, the job requires technical expertise to ensure the correct positioning and polar orientation. It’s often best left to professionals.
Can the magnet in a speaker demagnetize?
While technically possible, it’s highly unlikely that the magnet in a speaker will demagnetize under normal conditions. Most speaker magnets are made of materials like neodymium or ferrite, which resist demagnetization.
Does the size of the magnet affect speaker performance?
Absolutely, the size and weight of a speaker’s magnet can influence the speaker’s overall performance. Larger magnets typically result in a more powerful magnetic field, leading to better speaker performance.
Why aren’t all speaker magnets made of neodymium?
While neodymium magnets are more powerful and lighter than ferrite magnets, they’re also more expensive. As such, many manufacturers opt for using ferrite magnets in an effort to keep production costs down.
Does the placement of the magnet matter in a speaker?
Definitely, the magnet has to be perfectly positioned in relation to the voice coil for the speaker to function effectively. Incorrect placement can lead to distorted sound or no sound at all.
What’s the function of a speaker’s voice coil?
The voice coil in a speaker interacts with the magnetic field created by the magnet. When the voice coil carries an electrical signal, it creates a secondary magnetic field, which interacts with the primary field to produce movement. This movement is ultimately what we perceive as sound.
Are speaker magnets always circular?
Most speaker magnets are circular to ensure a uniform distribution of the magnetic field. However, one could find non-circular magnets in some specialized or proprietary speaker designs.
Do all speakers use permanent magnets?
Yes, all speakers use permanent magnets, as they produce the static magnetic fields needed for the voice coil to work. Temporary or electromagnets aren’t suitable due to inconsistent and unstable field behavior.

Hey there! I’m Henry Jack, the voice behind speakerrealm.com, your ultimate destination for everything speakers. Whether you’re a seasoned audio enthusiast or just starting to explore the world of sound, you’ve come to the right place.
At Speaker Realm, I dive deep into the realm of speakers, bringing you comprehensive reviews, insightful guides, and the latest trends in the industry. From floor-standing behemoths to compact bookshelf wonders, I cover it all.
I’m passionate about helping you find the perfect speakers to elevate your audio experience. Whether you’re setting up a home theater, upgrading your sound system, or just looking for some quality audio gear, I’ve got you covered.
But Speaker Realm isn’t just about technical specs and performance metrics—it’s also about the art and science of sound. I explore topics like acoustic design, speaker technology, and the impact of audio on our lives.
So whether you’re a casual listener or a hardcore audiophile, join me on this journey through the world of speakers. Let’s turn up the volume and explore the endless possibilities of sound together at speakerrealm.com!







